What is long and short position in forex trading
Understanding long and short positions is crucial for anyone involved in forex trading. A long position involves buying a currency pair with the expectation that its value will rise, while a short position entails selling a currency pair in anticipation of a decline in its value. Mastering these concepts allows traders to effectively strategize and take advantage of market movements, regardless of the direction in which the market is heading.
Understanding forex trading
The forex market operates through a network of banks, brokers, and financial institutions, allowing participants to buy, sell, exchange, and speculate on currencies. The primary objective of forex trading is to profit from the fluctuations in exchange rates between different currencies.
In forex trading, currencies are quoted in pairs, known as currency pairs. Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. For instance, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the U.S. dollar (USD) is the quote currency. The exchange rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. Traders speculate on whether the base currency will strengthen or weaken against the quote currency.
Several key terms and concepts are fundamental to understanding forex trading positions:
- Pip: A pip is the smallest price movement in a currency pair, typically equal to 0.0001 for most pairs.
- Spread: The spread is the difference between the bid (buy) and ask (sell) price of a currency pair.
- Leverage: Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, amplifying both potential profits and risks.
- Margin: Margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position.
What is a long position in forex trading?
A long position in forex trading involves buying a currency pair with the expectation that its value will rise over time. When a trader takes a long position, they are essentially betting that the base currency in the pair will appreciate relative to the quote currency.
Here's how a long position works: Suppose a trader believes that the euro (EUR) will strengthen against the U.S. dollar (USD). They would buy the EUR/USD currency pair. If the exchange rate increases, meaning the euro appreciates relative to the dollar, the trader can sell the pair at a higher price, thus making a profit from the difference in the buying and selling price.
For example, if a trader buys the EUR/USD pair at 1.1000 and the rate rises to 1.1200, the trader can close the position and realize a profit of 200 pips (the smallest unit of price movement in forex).
What is a short position in forex trading?
A short position in forex trading is initiated when a trader sells a currency pair, anticipating that its value will decrease. In this scenario, the trader is essentially wagering that the base currency will decline in value relative to the quote currency.
To illustrate, consider a trader who predicts that the Japanese yen (JPY) will rise against the U.S. dollar (USD). The trader would sell the USD/JPY currency pair. If the exchange rate falls, indicating the dollar has weakened against the yen, the trader can repurchase the pair at a lower rate, thereby securing a profit from the difference.
For example, if a trader sells the USD/JPY pair at 110.00 and the rate drops to 108.00, they can close the position with a profit of 200 pips, which is the smallest increment of price movement in forex trading.
Taking a short position has several benefits. It enables traders to capitalize on declining market trends and adverse economic conditions affecting the base currency. Additionally, short positions can act as a protective measure against other trades that might suffer losses if the base currency appreciates. Leveraging in forex trading allows traders to amplify potential gains from even slight price changes, provided they employ effective risk management strategies.
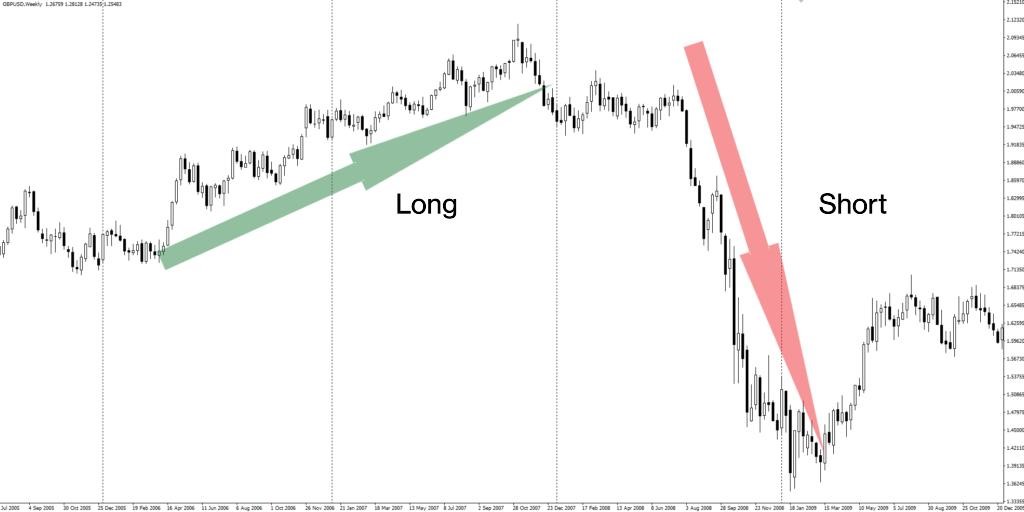
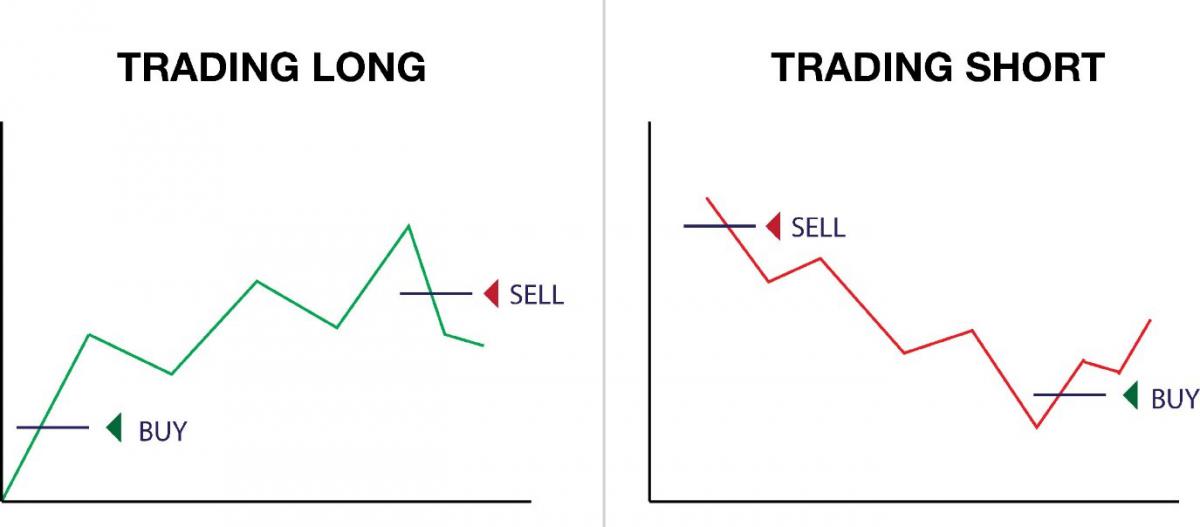
Long vs short position in forex
Understanding the key differences between long and short positions is essential for effective forex trading. A long position involves buying a currency pair with the expectation that its value will increase, allowing the trader to sell it later at a higher price. Conversely, a short position entails selling a currency pair in anticipation of a decrease in its value, so the trader can buy it back at a lower price.
When deciding whether to take a long or short position, traders consider several factors. Market trends are a primary consideration; in a bullish market, long positions are typically favored, while in a bearish market, short positions may be more advantageous. Economic indicators, such as interest rates, inflation rates, and employment data, also play a crucial role. Positive economic data for a country often leads to currency appreciation, making long positions more attractive, while negative data can result in depreciation, favoring short positions.
Geopolitical events and market sentiment are additional factors that influence trading decisions. Political instability, trade conflicts, or unexpected news can create market volatility, presenting opportunities for both long and short positions depending on the anticipated direction of currency movements.
Risk management in long and short positions
Risk management is a crucial aspect of forex trading, as it helps traders protect their capital and minimize potential losses. Effective risk management ensures that traders can sustain their trading activities over the long term, regardless of market volatility or unexpected events.
Several strategies can be employed to manage risk in both long and short positions. One fundamental strategy is setting stop-loss orders, which automatically close a position when the market moves against the trader by a specified amount. This prevents significant losses and protects the trader’s investment. Another essential strategy is position sizing, where traders determine the amount of capital to allocate to each trade based on their overall risk tolerance and trading goals. This approach helps in controlling potential losses by not risking too much on a single trade.
Diversification is another effective risk management technique. By spreading investments across different currency pairs, traders can reduce the impact of adverse movements in any one pair. Additionally, traders should stay informed about economic and geopolitical events that might affect the forex market, enabling them to make timely adjustments to their positions.
Tools and techniques for effective risk management are essential for maintaining control over trading activities. Technical analysis tools play a significant role in this process. Moving averages, for instance, smooth out price data to help identify trends over time, making it easier to determine optimal entry and exit points. The relative strength index (RSI) measures the speed and change of price movements, indicating overbought or oversold conditions that can signal potential reversals. Additionally, risk-reward ratios are crucial, as they guide traders to pursue trades where the potential profit significantly outweighs the potential loss. By setting a target reward that is at least twice the potential risk, traders can improve their chances of achieving profitable outcomes. Employing these tools and techniques helps traders make more informed decisions and manage their risk more effectively.
Common mistakes to avoid
In forex trading, avoiding common mistakes can significantly improve a trader's performance and profitability. Both long and short positions come with their own sets of pitfalls that traders should be aware of.
When taking long positions, traders often make the mistake of entering trades based on emotions rather than analysis. Overconfidence in a bullish trend can lead to overleveraging, where traders risk more than they can afford to lose. Another common error is failing to set stop-loss orders, leaving positions vulnerable to sudden market reversals.
Similarly, short positions carry their own risks. One frequent mistake is shorting a currency pair without thoroughly understanding the underlying economic and geopolitical factors that could influence its movement. Traders might also hold onto losing short positions for too long, hoping the market will turn in their favor, which can lead to substantial losses.
To avoid these mistakes, traders should adhere to a disciplined approach. Conducting thorough market analysis before entering any trade is essential. This includes using technical and fundamental analysis to make informed decisions. Setting stop-loss orders is crucial for both long and short positions to limit potential losses. Additionally, maintaining a risk management plan and avoiding overleveraging can help traders stay within their risk tolerance levels.
Famous case studies in forex trading
Studying well-known case studies of long and short positions can provide valuable insights into successful trading strategies and the potential pitfalls to avoid. Here, we explore two of the most famous cases in forex trading history.
Famous case study of a long position: George Soros and the British Pound (1992)
In 1992, George Soros made a legendary long position on the British pound, which is famously known as "Black Wednesday." Soros believed that the British pound was overvalued and that the United Kingdom would be forced to withdraw from the European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM).
Soros's hedge fund, Quantum Fund, began accumulating a massive long position on the British pound. As pressure mounted on the Bank of England to devalue the pound or leave the ERM, Soros increased his position. On September 16, 1992, known as Black Wednesday, the British government withdrew from the ERM and devalued the pound. Soros’s position paid off handsomely, netting him an estimated $1 billion in profits.
This case study highlights the importance of thorough analysis and conviction in a trading strategy. Soros’s understanding of the economic situation and his willingness to take a significant position led to one of the most famous trades in history.
Famous case study of a short position: The Yen Carry trade (2007-2008)
The Yen Carry Trade, prominent in the early 2000s, involved borrowing Japanese yen at low-interest rates and investing in higher-yielding currencies, such as the Australian dollar. This trade was widely popular due to the significant interest rate differential between Japan and other countries.
However, during the financial crisis of 2007-2008, the strategy backfired. As global financial markets became highly volatile, traders began unwinding their carry trades, leading to a sharp appreciation of the yen. Those who were heavily short on the yen faced substantial losses as they scrambled to cover their positions.
The unwinding of the Yen Carry Trade is a classic example of the risks associated with short positions, especially in times of market turmoil. It underscores the importance of risk management and the need to be aware of broader economic and market conditions that can drastically affect currency values.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding long and short positions is fundamental to successful forex trading. Long positions involve buying a currency pair with the expectation that its value will rise, while short positions involve selling a currency pair anticipating a decline in value. These strategies allow traders to profit from both upward and downward market movements, making them versatile tools in a trader's arsenal.
Famous case studies, such as George Soros's long position on the British pound and the Yen Carry Trade, illustrate the profound impact that well-informed, strategic trading decisions can have. These examples underscore the importance of thorough analysis, risk management, and staying informed about market conditions.
By staying informed and honing their skills, traders can more confidently and successfully navigate the complexities of the forex market.


