Volatility indicators list
Volatility is a fundamental concept in the forex market, reflecting the pace and magnitude of price movements over time. It serves as a critical metric for traders, helping them identify market dynamics and adjust their strategies accordingly. High volatility often signals significant trading opportunities, while low volatility may indicate stability or a lack of market momentum. For forex traders, understanding and monitoring volatility is essential for effective risk management and decision-making.
Volatility indicators play a pivotal role in navigating these price fluctuations. These tools offer insights into the intensity of market activity, allowing traders to anticipate potential breakout or reversal scenarios. By incorporating volatility indicators into their trading plans, traders can better assess when to enter or exit trades, set stop-loss levels, and determine optimal position sizes.
What are volatility indicators?
Volatility indicators are essential tools in forex trading, designed to measure and interpret the degree of price fluctuation in the market over a specific period. Unlike trend indicators that focus on the direction of price movements or momentum indicators that assess the speed of these changes, volatility indicators provide insights into the intensity and variability of price activity. By analyzing volatility, traders can determine whether a currency pair is experiencing stable or turbulent market conditions, which is critical for making informed trading decisions.
These indicators are particularly valuable because volatility often signals shifts in market sentiment. Periods of high volatility can indicate increased uncertainty or significant news events that drive sharp price movements, while low volatility suggests a quieter market with limited trading opportunities. For traders, understanding these patterns helps in timing trades effectively and managing risks more efficiently.
For instance, volatility indicators can help identify potential breakout scenarios where price moves significantly outside a defined range. Similarly, they can highlight periods when market activity is contracting, signaling the possibility of consolidation before a major price movement.
Many volatility indicators, such as Bollinger Bands or the Average True Range (ATR), are built into popular trading platforms, making them accessible even to beginner traders. They can be used independently or in conjunction with other technical tools to provide a holistic view of market conditions.
The importance of using volatility indicators in forex
Volatility indicators are indispensable tools for forex traders, offering a deeper understanding of market dynamics. By providing a measure of price variability, they help traders assess the intensity of market activity and anticipate potential changes in trading conditions. This information is vital for crafting effective strategies, managing risks, and seizing profitable opportunities in a fast-paced trading environment.
In forex trading, volatility acts as both an opportunity and a challenge. High volatility periods often signal increased trading opportunities due to significant price movements, enabling traders to capitalize on rapid market shifts. However, such periods also come with heightened risks, as sudden price reversals can lead to unexpected losses. Conversely, low volatility environments may indicate a lack of momentum, often requiring traders to adjust their strategies or exercise patience until the market shows signs of activity.
Volatility indicators help traders navigate these complexities by offering objective data on market conditions. For example, tools like the Average True Range (ATR) help traders set realistic stop-loss levels, ensuring adequate protection against unexpected price swings. Bollinger Bands, another popular indicator, provide visual cues about price compression and potential breakout scenarios, helping traders identify entry and exit points with greater precision.
Popular volatility indicators
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are a popular volatility indicator consisting of a simple moving average (SMA) and two bands plotted above and below it. These bands expand and contract based on market volatility, providing a visual representation of price action. When the bands are wide, the market is volatile; when they narrow, it signals reduced activity. Traders use Bollinger Bands to identify breakouts and overbought or oversold conditions, making them a versatile tool for market analysis.
Average True Range (ATR)
The Average True Range is a straightforward indicator that measures market volatility by calculating the average range between high and low prices over a specified period. ATR does not indicate price direction but provides insights into the strength of price movements. Forex traders often use ATR to set stop-loss levels, ensuring they align with prevailing market conditions.
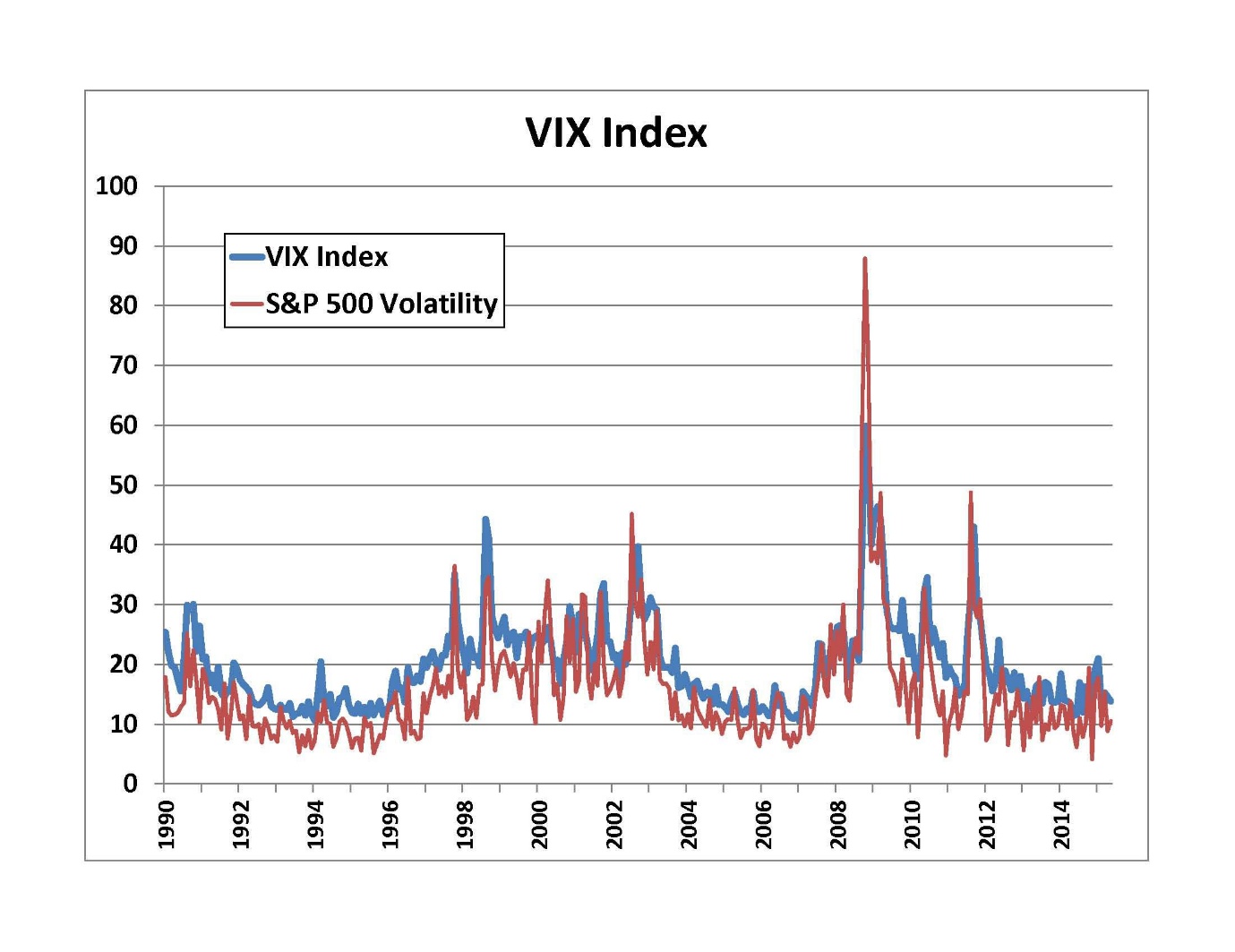
Volatility Index (VIX)
While primarily associated with equity markets, the Volatility Index, or VIX, is an essential tool for understanding global market sentiment. In forex, traders use the VIX to gauge risk appetite and predict potential volatility in currency pairs correlated with broader financial markets.
Keltner Channels
Similar to Bollinger Bands, Keltner Channels use ATR and exponential moving averages to measure volatility. Traders often compare the two to identify subtle differences in market conditions and refine their strategies.
Advanced volatility indicators to consider
While commonly used volatility indicators like Bollinger Bands and ATR provide foundational insights, advanced tools offer nuanced ways to measure and interpret market activity. These indicators are especially useful for experienced traders looking to refine their strategies in the forex market.
Chaikin Volatility
Developed by Marc Chaikin, Chaikin Volatility focuses on changes in the volatility of the accumulation/distribution line over a specified period. It emphasizes the speed at which prices change rather than the actual price levels. By tracking these fluctuations, traders can identify periods of accumulation or distribution that often precede significant market moves.
Standard Deviation
Standard Deviation is a statistical measure used to assess the dispersion of price data from its average value. A higher standard deviation indicates greater volatility, while a lower value suggests a more stable market. Traders often use this indicator in conjunction with other tools, such as Bollinger Bands, to confirm breakout signals and evaluate market risk.
Historical Volatility (HV)
Historical Volatility examines past price movements to estimate future volatility levels. It is calculated using statistical models that analyze price data over a set period. This indicator is particularly valuable for identifying long-term market trends and assessing risk in specific currency pairs.
How to incorporate volatility indicators into a trading strategy
Integrating volatility indicators into a trading strategy can significantly enhance decision-making and risk management. These tools provide traders with actionable insights into market conditions, enabling them to tailor their approaches to both high-volatility and low-volatility environments.
Combining volatility and trend indicators
Volatility indicators work best when paired with other tools, such as trend indicators. For instance, traders might use Bollinger Bands to identify periods of price compression, followed by a moving average crossover to confirm breakout direction. This combination ensures a more holistic analysis, reducing the risk of false signals.
Adapting to trading styles
Volatility indicators can be customized to align with different trading styles. Scalpers, for example, might rely on tools like the Average True Range (ATR) to quickly assess intraday price movements, while swing traders may use Bollinger Bands or Keltner Channels to identify potential reversals over longer time frames. Understanding the indicator’s time frame compatibility is key to maximizing its effectiveness.
Setting stop-loss and take-profit levels
One of the most practical uses of volatility indicators is in defining stop-loss and take-profit levels. Tools like ATR help traders set dynamic stop-losses based on current market conditions, ensuring protection against unexpected price swings without cutting trades short prematurely.
Backtesting and refining strategies
Traders should always test their strategies in demo accounts or using historical data before applying them in live markets. This allows them to refine their approach and gain confidence in their use of volatility indicators.
Common mistakes when using volatility indicators
Over-reliance on a single indicator
One of the most frequent mistakes traders make is relying solely on a single volatility indicator to make trading decisions. For example, using only Bollinger Bands might provide insight into price compression but won’t indicate the direction of the breakout. Combining volatility tools with trend or momentum indicators provides a more balanced and informed perspective.
Misinterpreting high and low volatility
Traders often mistake high volatility as a signal for guaranteed profit opportunities. While high volatility can present significant trading chances, it also comes with increased risk of rapid price reversals. Conversely, low volatility may lead to stagnation, but it can also precede strong breakouts. Recognizing these nuances is essential for effective decision-making.
Ignoring broader market context
Volatility indicators should never be used in isolation from broader market analysis. For instance, external factors such as geopolitical events, economic reports, or central bank decisions often drive market volatility. Neglecting these influences can result in misaligned strategies and unexpected losses.
Failing to adjust settings
Default indicator settings may not suit every trading style or market condition. Traders should customize parameters like period lengths in tools like the Average True Range (ATR) or Bollinger Bands to match their trading objectives and market environments.
Conclusion
Volatility indicators are indispensable tools in the arsenal of forex traders, providing critical insights into the intensity and variability of market price movements. By analyzing volatility, traders gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics, enabling them to adapt their strategies to both stable and unpredictable conditions.
However, as with any tool, the key to maximizing the value of volatility indicators lies in their proper application. Traders should avoid common mistakes, such as over-reliance on a single indicator or ignoring broader market contexts, and instead strive to integrate volatility analysis with other technical tools and fundamental insights. Customizing indicator settings and thoroughly testing strategies in demo environments can further enhance their effectiveness.


