Gap trading strategy in forex
Gaps in the forex market typically occur due to external factors, such as geopolitical events, economic data releases, or changes in market sentiment over weekends when the forex market is closed. For traders, these gaps can signal potential reversals, trend continuations, or even a market’s overreaction. However, identifying and trading gaps effectively requires knowledge, skill, and the right tools.
Platforms like MetaTrader (MT4/MT5) are invaluable for analyzing gaps and planning trades, offering advanced charting tools and historical data for backtesting strategies. Moreover, staying informed through trusted sources like Reuters, DailyFX, and Investing.com ensures traders are aware of the events that often lead to gaps.
A gap trading strategy is not just about recognizing these price gaps; it is about interpreting them correctly, implementing proper risk management, and using a disciplined trading plan.
What Is gap trading in forex?
Gap trading in forex refers to a strategy that seeks to capitalize on price gaps—abrupt shifts in price between trading sessions. Unlike the continuous price flow seen during active forex market hours, gaps represent areas on a price chart where no trading activity occurs, creating a visible discontinuity. While gaps are more frequent in equity and commodity markets due to their fixed trading hours, they also occur in forex, especially during the transition from the market's weekend closure to its reopening.
There are four primary types of gaps observed in trading:
Common gaps
These are minor gaps that often occur without significant market-driving news and are typically filled quickly as the market returns to its prior price levels.
Breakaway gaps
These signal the start of a new trend, often triggered by major news or fundamental shifts, such as central bank announcements or geopolitical events.
Runaway gaps
Found within strong trends, these gaps confirm market momentum and suggest that the trend will continue.
Exhaustion gaps
These appear at the end of a trend and may indicate a pending reversal as the market becomes overextended.
In the forex market, gaps are often caused by weekend developments, such as macroeconomic reports or political events, which influence currency values before markets reopen. For instance, significant news regarding central bank policy from entities like the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank can lead to sharp price changes.
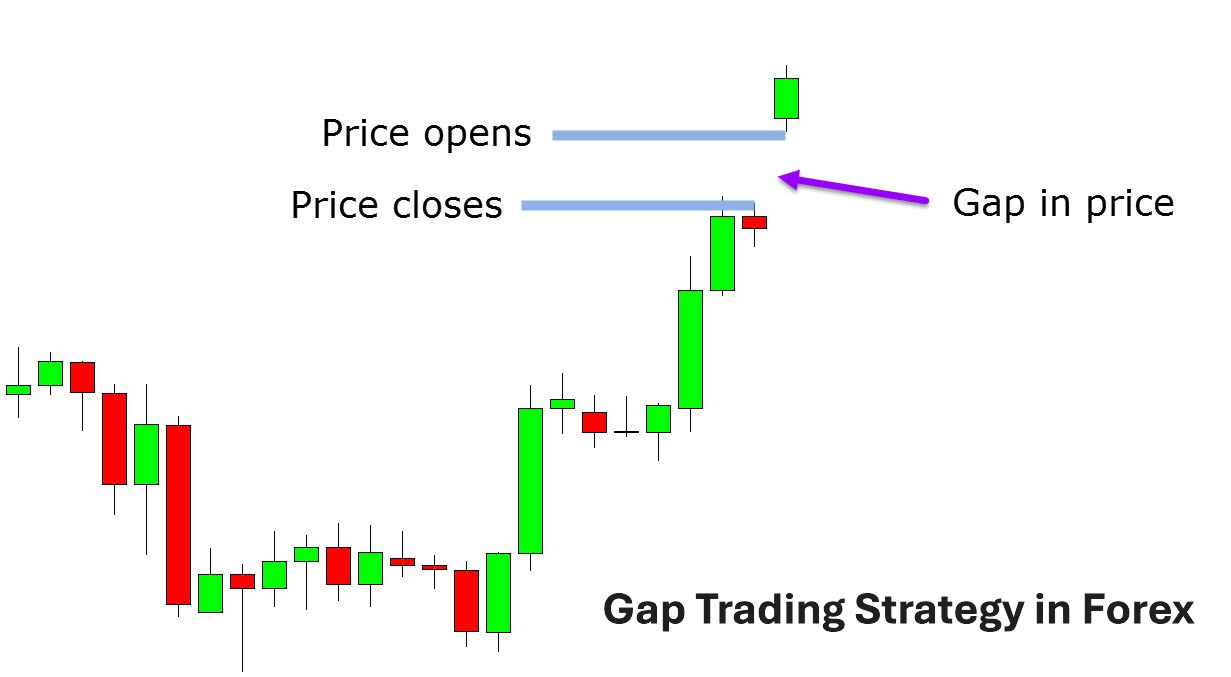
Why do gaps happen in forex markets?
Gaps in the forex market occur when there is a significant disparity between the closing price of a currency pair at the end of one trading session and its opening price at the start of the next. While forex is a 24-hour market during the weekdays, it closes over the weekend. During this downtime, developments in the global economy, politics, or other external factors can lead to dramatic shifts in currency valuations, resulting in gaps when the market reopens. Understanding the reasons behind these gaps is important for traders aiming to incorporate them into their strategies.
One of the most common causes of forex gaps is weekend price movement. Events such as political elections, natural disasters, or geopolitical conflicts often unfold when the forex market is closed. For instance, a surprising election result or a central bank announcement can lead to a sharp repricing of currency pairs by market participants before the next trading session begins.
Another major driver of gaps is economic news releases. High-impact reports, such as U.S. non-farm payrolls, GDP data, or interest rate decisions by institutions like the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank, often spark sudden market reactions. If traders fail to anticipate or price in these developments, gaps can emerge.
Finally, liquidity and volatility play a significant role. Gaps are more likely to occur during periods of low liquidity, such as the opening of the forex market after the weekend, when fewer traders are active. This mismatch between supply and demand can cause sudden price surges or drops.
Gap trading strategies in forex
Gap trading strategies in forex are designed to help traders profit from the price movements associated with gaps. These strategies are rooted in the belief that gaps, depending on their type, can signal specific market behaviors, such as reversals, trend continuations, or new trends.
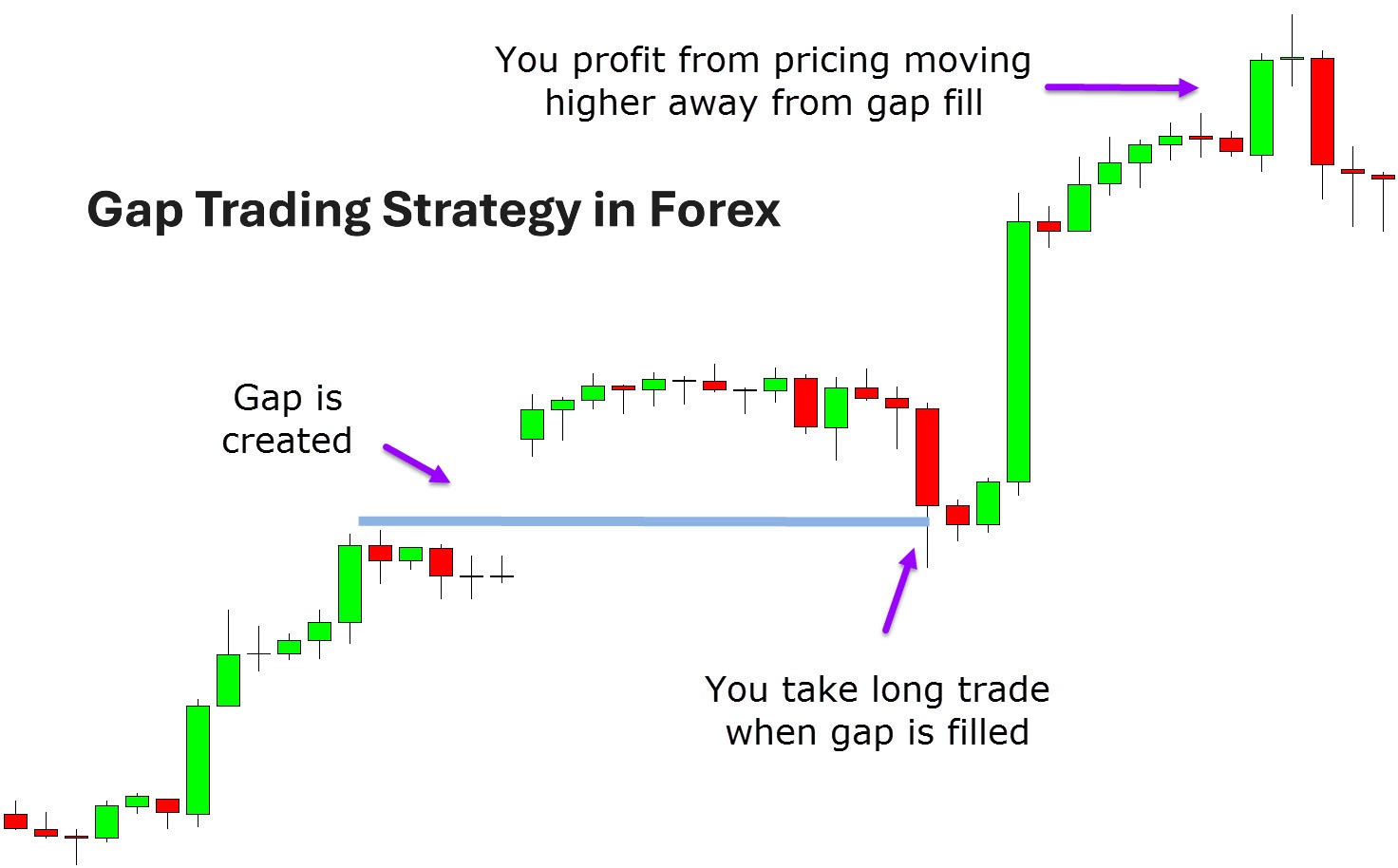
Gap-filling strategy
This strategy focuses on the idea that gaps often “close” or “fill,” meaning the price returns to the level where the gap originated. For example, if the EUR/USD opens higher on Monday due to weekend developments, a trader may anticipate the price dropping to Friday’s closing level, especially if there is no strong trend or news sustaining the upward movement. Tools like Fibonacci retracements or support/resistance levels on platforms like TradingView can aid in this analysis.
Breakaway gap strategy
Breakaway gaps occur when the market moves sharply out of a consolidation zone, signaling the start of a new trend. Traders using this strategy look for gaps following major news, such as an interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve, and trade in the direction of the breakout.
Trend continuation with runaway gaps
Runaway gaps appear in the middle of strong trends, confirming market momentum. Traders often use indicators like moving averages or RSI to validate the trend and place trades aligned with the market’s direction.
Exhaustion gap reversals
Exhaustion gaps occur at the end of a trend, signaling potential reversals. By analyzing volume and candlestick patterns, traders can identify opportunities to trade in the opposite direction of the prior trend.
Key tools and indicators for gap trading
Successful gap trading in forex requires more than just identifying gaps; it depends on using the right tools and indicators to interpret them and execute trades effectively.
Support and resistance levels
Support and resistance zones are critical in gap trading. When a gap occurs near a strong support or resistance level, it can provide insight into whether the gap is likely to fill or continue. For instance, a breakaway gap above resistance often signals the start of a new trend, while a gap near support might close as the market pulls back.
Volume analysis
Volume can help confirm the significance of a gap. For example, a breakaway gap with high trading volume indicates strong market conviction, while a gap with low volume might suggest hesitation or a potential reversal. Volume data is readily available on platforms like MetaTrader and TradingView.
Fibonacci retracement levels
Fibonacci retracements are useful for predicting potential price movements after a gap. Traders can apply these levels to analyze whether a gap might retrace to certain percentages (e.g., 38.2% or 61.8%) before continuing in its original direction.
Moving averages (MA)
Moving averages are commonly used to identify trends and confirm runaway gaps. For example, when a gap occurs above a rising MA, it often signals trend continuation. Crossovers can provide additional entry or exit points.
Candlestick patterns
Candlestick patterns, such as engulfing or doji formations, help traders interpret the strength or weakness of a gap. For example, an exhaustion gap near a bearish reversal pattern might indicate a trend is losing momentum.
Risk management in gap trading
While gaps can present lucrative opportunities, they also carry significant risks due to their unpredictable nature. Without a structured approach to risk management, traders may face substantial losses, especially in volatile markets.
Setting stop-loss and take-profit levels
Stop-loss orders are essential in gap trading to limit potential losses if the market moves against the trader’s position. For instance, when trading a gap-fill strategy, a stop-loss can be placed just beyond the gap to protect against unexpected breakouts. Similarly, take-profit levels should be predetermined to lock in gains, such as at the previous closing price in a gap-fill scenario.
Position sizing
Proper position sizing is critical to managing risk. Traders should avoid over-leveraging and ensure their position sizes align with their risk tolerance and account size. A common approach is to risk no more than 1-2% of total account equity on a single trade.
Avoiding over-leveraging
Leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses. Given the rapid and sometimes volatile nature of gaps, excessive leverage can quickly lead to large losses. Traders are encouraged to use leverage conservatively, particularly when trading on platforms like MetaTrader or Forex.com.
Adapting to market conditions
Market conditions can change rapidly, especially during periods of heightened volatility. Traders should regularly monitor news from trusted sources like Reuters, Bloomberg, and DailyFX to stay informed about developments that could impact currency pairs and create gaps.
Conclusion
Gap trading in forex is a useful and strategic approach that can provide traders with valuable opportunities to profit from sudden price movements. While gaps may not be as frequent in forex as they are in equity markets, they still occur under specific conditions, such as after weekend market closures or during significant economic events. For traders who are equipped with the right knowledge, tools, and strategies, gap trading can be an effective way to navigate the forex market’s inherent volatility.
The key to success in gap trading lies in understanding the different types of gaps—common, breakaway, runaway, and exhaustion—and knowing how to interpret their implications. Whether applying a gap-fill strategy to capture price corrections or using a breakaway gap strategy to follow a new trend, traders need to back their decisions with sound technical analysis and a structured trading plan.


